
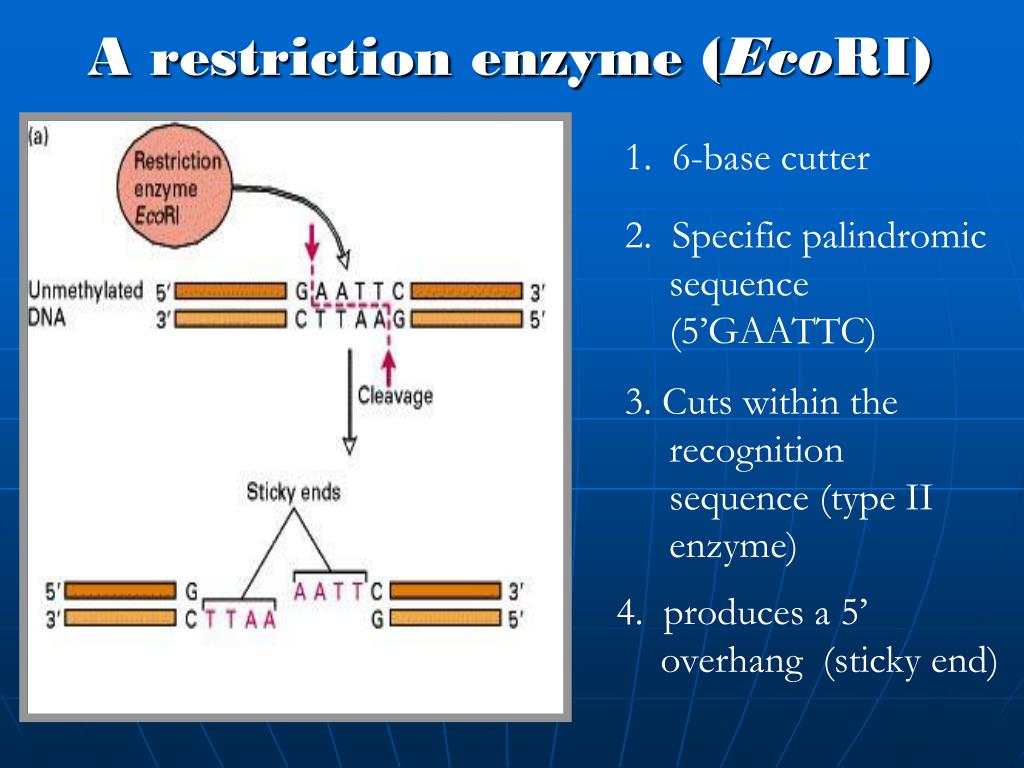
This specific mode of action of Type IIS restriction enzymes is widely used for innovative DNA manipulation techniques, such as.

Cold Spring Harbor: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory. a) Identify the palindromic sequence in the duplex DNA molecule shown below. Type IIS restriction enzymes comprise a specific group of enzymes which recognize asymmetric DNA sequences and cleave at a defined distance outside of their recognition sequence, usually within 1 to 20 nucleotides. REBASE – Enzymes and genes for DNA restriction and modification. J., Vincze, T., Posfai, J., & Macelis, D. Insertions, deletions, and single-nucleotide polymorphisms at rare restriction enzyme sites enhance discriminatory power of polymorphic amplified typing sequences, a novel strain typing system for Escherichia coli O157: H7. The human genome has many palindromic sequences distributed throughout. Palindromic sequences are found in abundance in the genome of most organisms. There are several ways to classify restriction enzymes. This means the short recognition sequence reads the same way on both strands resulting in the enzyme cutting both strands of a double-stranded DNA molecule. Bacteriophage survival: Multiple mechanisms for avoiding the deoxyribonucleic acid restriction systems of their hosts. The recognition sequence of few restriction enzymes is given below: DNA Replication, Gene Regulation and Expression Palindromic sequences have great significance. restriction sites: specific sequences of nucleotides, which are recognized by restriction enzymes. An important aspect of restriction recognition sites is that they are palindromic. Specificity of restriction endonucleases and DNA modification methyltransferases a review (edition 3). A robust, simple genotyping-by-sequencing (GBS) approach for high diversity species. American Journal of Human Genetics, 32(3), 314.Įlshire, R. Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Annual Review of Biochemistry, 38, 467–500.īotstein, D., White, R.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
